
Entity-Purchase Buy-Sell Arrangements
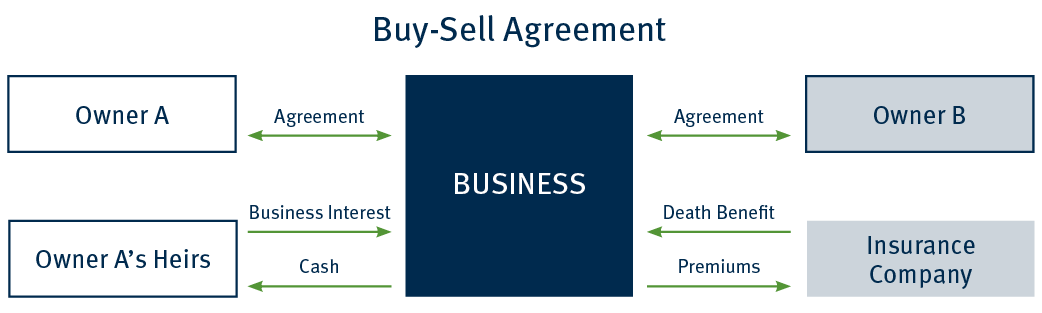
A buy-sell agreement identifies a buyer for a business in the event of an owner’s death. In an entity-purchase arrangement, the business is obligated to purchase the interest of a departing owner. To fund the buyout, the business is the owner, premium payor, and beneficiary of a life insurance policy on the life of each owner. Upon an owner’s death, the business receives the life insurance death benefit and purchases the deceased business owner’s interest from the estate. The surviving owners retain control of the business, and the non-liquid business interest is converted to cash for the heirs.
Client Profile
- Business with more than two owners
Why It Is Used
- Guarantees a market for future sale of the business
- Guarantees business interest passes only to the business
- Minimizes number of life insurance policies required
- Provides fair market value for deceased owner’s heirs
- Provides liquidity for the family of a deceased owner
Advantages
- Guarantees a purchaser for the business
- Provides liquidity to meet purchase obligation
- Surviving owner(s) retain control of the business
- Terms of sale negotiated prior to death
- Heirs of deceased owner receive fair market value
- Family of a deceased owner receives cash to pay estate taxes and/or to meet family needs
- Assurance of continued operation for creditors and employees
- Requires only one life insurance policy on each owner
Disadvantages
- Transfer of policies to surviving owners may cause proceeds to be taxed as ordinary income
- Purchase of less than stockholder’s entire interest may cause proceeds to be taxed as ordinary income
Role of Life Insurance
- Provides liquidity to meet purchase obligation
- Provides immediate full funding of the purchase price
- Less costly funding method than borrowing the funds or using the company’s working capital
- Leverages premium dollars
Tax Considerations
- Premiums not income tax deductible
- No step-up in basis for surviving owners
- Stock redemptions are subject to attribution rules
- Death benefit subject to income tax unless notice and consent requirements are followed
- Life insurance cash value and death benefit may be subject to corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT)
IRS CIRCULAR 230 DISCLOSURE: To ensure compliance with the requirements imposed by IRS Circular 230, we inform you that to the extent this communication, including attachments, mentions any federal tax matter, it is not intended or written and cannot be used for the purpose of avoiding Federal Tax penalties. In addition, this communication may not be used by anyone in promoting, marketing, or recommending the transaction or matter addressed herein. Anyone other than the recipient who reads this communication should seek advice based on their particular circumstances from an independent tax advisor. Stifel does not provide legal or tax advice.
0621.3124969.2